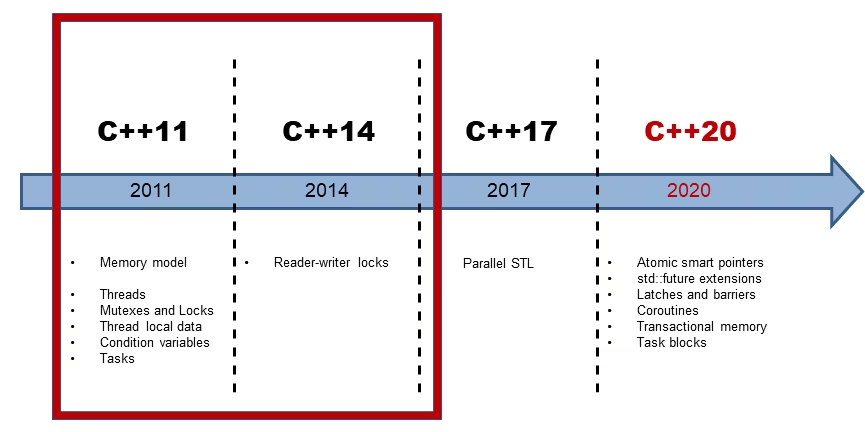
Cpp Timeline
C++: 从 C++11 到 C++23 的演进之路
C++ 从 2011 年开始进入了快速发展的时代,每三年一个新标准,带来了大量现代特性。本文将梳理 C++11 到 C++23 的主要特性和常用特性。
C++11
| Core Feature | Library | Concurrency |
|---|---|---|
C++14
| Core Feature | Library | Concurrency |
|---|---|---|
C++17
| Core Feature | Library | Concurrency |
|---|---|---|
C++20
| The Big | Core Feature | Library | Concurrency |
|---|---|---|---|
C++23
| Core Feature | Library | Concurrency |
|---|---|---|
|
C++11:现代 C++ 的开端
C++11 是 C++ 历史上最重要的标准之一,它彻底改变了 C++ 的编程方式,被称为"现代 C++"的起点。
自动类型推导(auto)
auto x = 42; // int
auto y = 3.14; // double
auto z = std::vector<int>{1, 2, 3}; // std::vector<int>
// 范围 for 循环
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (auto& elem : vec) {
elem *= 2;
}Lambda 表达式
// 基本语法
auto lambda = [](int x, int y) { return x + y; };
int result = lambda(3, 4); // 7
// 捕获变量
int a = 10;
auto captureByValue = [a](int x) { return x + a; };
auto captureByRef = [&a](int x) { a += x; };
// 捕获所有
auto captureAll = [=](int x) { return x + a; };
auto captureAllRef = [&](int x) { a += x; };智能指针
#include <memory>
// unique_ptr:独占所有权
std::unique_ptr<int> ptr1 = std::make_unique<int>(42);
// std::unique_ptr<int> ptr2 = ptr1; // 编译错误
// shared_ptr:共享所有权
std::shared_ptr<int> ptr3 = std::make_shared<int>(42);
std::shared_ptr<int> ptr4 = ptr3; // 引用计数 +1
// weak_ptr:弱引用,不增加引用计数
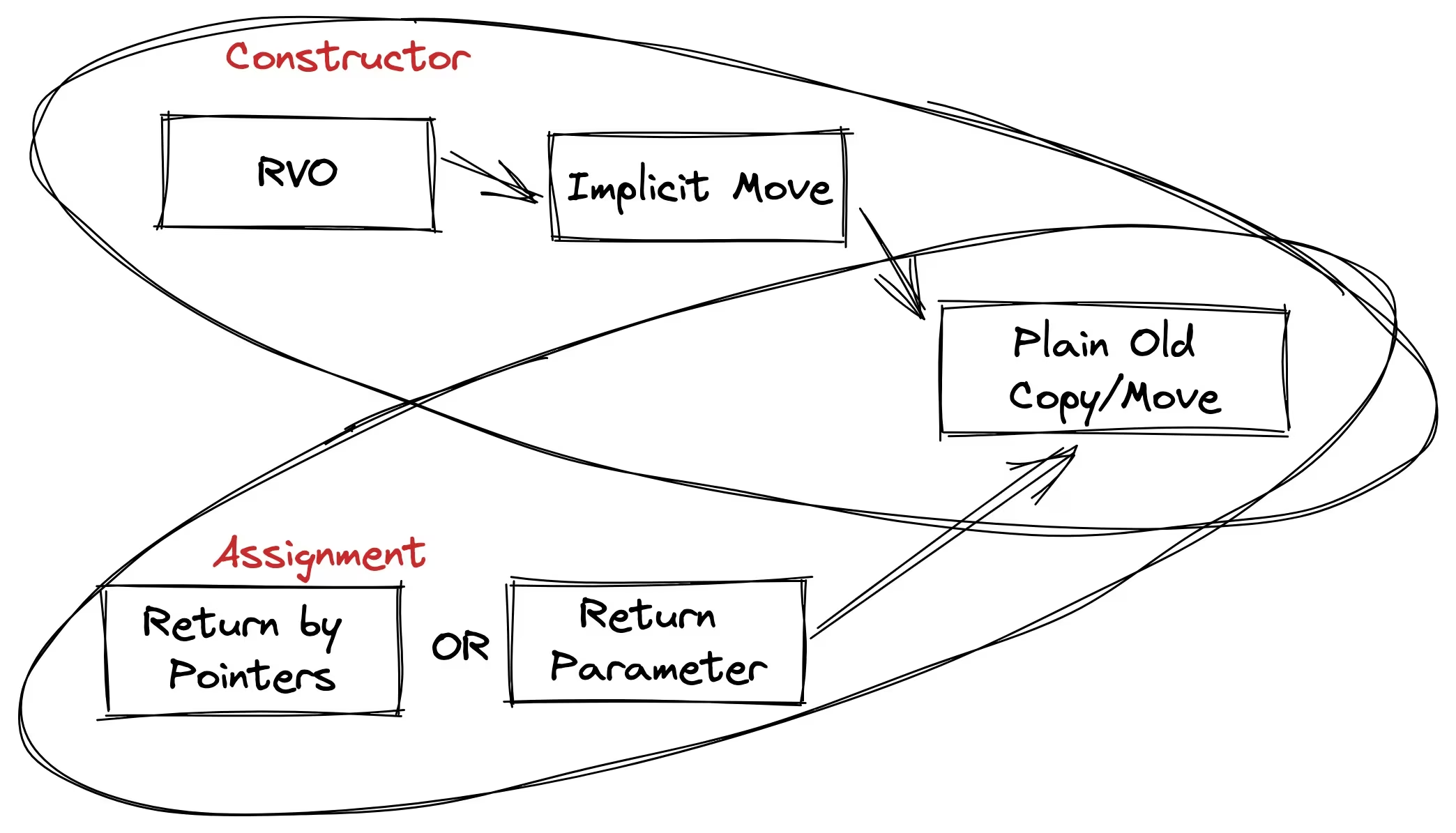
std::weak_ptr<int> ptr5 = ptr3;右值引用与移动语义
// 移动构造函数
class MyClass {
public:
MyClass(MyClass&& other) noexcept
: data_(std::move(other.data_)) {
other.data_ = nullptr;
}
// 移动赋值运算符
MyClass& operator=(MyClass&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
delete data_;
data_ = std::move(other.data_);
other.data_ = nullptr;
}
return *this;
}
private:
int* data_;
};
// std::move
std::string str1 = "Hello";
std::string str2 = std::move(str1); // str1 现在为空std::function 和 std::bind
#include <functional>
int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
// std::function:可调用对象的包装器
std::function<int(int, int)> func = add;
int result = func(3, 4); // 7
// std::bind:绑定参数
auto add5 = std::bind(add, std::placeholders::_1, 5);
int result2 = add5(10); // 15
// 绑定成员函数
struct Calculator {
int multiply(int a, int b) { return a * b; }
};
Calculator calc;
auto multiplyBy2 = std::bind(&Calculator::multiply, &calc, std::placeholders::_1, 2);
int result3 = multiplyBy2(5); // 10std::unordered_map 和 std::unordered_set
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
// 哈希表
std::unordered_map<std::string, int> scores;
scores["Alice"] = 90;
scores["Bob"] = 85;
// 查找
if (scores.find("Alice") != scores.end()) {
std::cout << "Alice's score: " << scores["Alice"] << "\n";
}
// unordered_set
std::unordered_set<int> uniqueValues = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3};
// uniqueValues = {1, 2, 3}std::tuple
#include <tuple>
// 创建 tuple
std::tuple<int, double, std::string> t{42, 3.14, "hello"};
// 获取元素
std::get<0>(t); // 42
std::get<1>(t); // 3.14
std::get<2>(t); // "hello"
// 结构化绑定(C++17)
auto [id, value, name] = t;
// 连接 tuple
auto combined = std::tuple_cat(t, std::make_pair(true, 'a'));std::chrono
#include <chrono>
// 时间点
auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
// duration
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
auto duration = 100ms; // 100 毫秒
auto seconds = 2s; // 2 秒
auto minutes = 5min; // 5 分钟
// 睡眠
std::this_thread::sleep_for(500ms);
// 计时
auto start = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
// ... 执行操作
auto end = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto elapsed = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(end - start);std::array
#include <array>
// 固定大小数组
std::array<int, 5> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 访问元素
arr[0] = 10;
arr.at(1) = 20;
// 迭代
for (const auto& elem : arr) {
std::cout << elem << " ";
}
// 大小
std::cout << "Size: " << arr.size() << "\n"; // 5
// 前后元素
std::cout << "Front: " << arr.front() << "\n";
std::cout << "Back: " << arr.back() << "\n";
// 填充
arr.fill(0);std::forward_list
#include <forward_list>
// 单向链表
std::forward_list<int> list = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 在前面插入
list.push_front(0);
// 在指定位置后插入
auto it = list.begin();
list.insert_after(it, 100);
// 删除元素
list.pop_front();
list.erase_after(it);
// 遍历
for (const auto& elem : list) {
std::cout << elem << " ";
}
// 检查是否为空
if (list.empty()) {
std::cout << "List is empty\n";
}std::random
#include <random>
// 随机数引擎
std::random_device rd; // 硬件随机数生成器
std::mt19937 gen(rd()); // Mersenne Twister 引擎
// 均匀分布
std::uniform_int_distribution<> dis(1, 100);
int randomInt = dis(gen); // 1-100 之间的随机整数
// 浮点数分布
std::uniform_real_distribution<> disReal(0.0, 1.0);
double randomDouble = disReal(gen);
// 正态分布
std::normal_distribution<> normal(5.0, 2.0);
double normalValue = normal(gen);
// 伯努利分布
std::bernoulli_distribution bernoulli(0.5);
bool coinFlip = bernoulli(gen);std::regex
#include <regex>
// 正则表达式匹配
std::string text = "Hello, World! 123";
std::regex pattern(R"(\d+)"); // 匹配数字
std::smatch matches;
if (std::regex_search(text, matches, pattern)) {
std::cout << "Found: " << matches[0] << "\n"; // 123
}
// 正则表达式替换
std::string result = std::regex_replace(text, std::regex(R"(\d+)"), "NUM");
std::cout << result << "\n"; // Hello, World! NUM
// 正则表达式迭代
std::regex word_pattern(R"(\w+)");
std::sregex_iterator it(text.begin(), text.end(), word_pattern);
std::sregex_iterator end;
for (; it != end; ++it) {
std::cout << it->str() << "\n";
}范围 for 循环
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 只读
for (const auto& elem : vec) {
std::cout << elem << " ";
}
// 修改
for (auto& elem : vec) {
elem *= 2;
}
// 数组
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3};
for (auto& x : arr) {
x *= 2;
}初始化列表
// 统一初始化
int x{42};
std::vector<int> vec{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::map<std::string, int> m{
{"apple", 1},
{"banana", 2}
};
// 防止窄化转换
// int y{3.14}; // 编译错误nullptr
void func(int* ptr) {}
void func(int x) {}
func(nullptr); // 调用 func(int*)
// func(NULL); // 可能有歧义
int* ptr = nullptr;constexpr
constexpr int factorial(int n) {
return n <= 1 ? 1 : n * factorial(n - 1);
}
constexpr int result = factorial(5); // 编译期计算类型别名
using String = std::string;
using IntVector = std::vector<int>;
// 模板别名
template<typename T>
using Vec = std::vector<T>;
Vec<int> v; // std::vector<int>委托构造函数
class MyClass {
public:
MyClass(int x, int y) : x_(x), y_(y) {}
// 委托给上面的构造函数
MyClass(int x) : MyClass(x, 0) {}
MyClass() : MyClass(0, 0) {}
private:
int x_, y_;
};override 和 final
class Base {
public:
virtual void func() {}
virtual void finalFunc() final {}
};
class Derived : public Base {
public:
void func() override {} // 明确表示重写
// void finalFunc() override {} // 编译错误,final 函数不能重写
};
class FinalClass final : public Base {
// 不能被继承
};enum class
enum class Color { Red, Green, Blue };
enum class Animal { Dog, Cat };
Color c = Color::Red;
// Color c2 = Red; // 编译错误,需要作用域
// if (c == Animal::Dog) {} // 编译错误,不同枚举类型不能比较
// 显式转换
int value = static_cast<int>(Color::Red); // 0静态断言
static_assert(sizeof(int) == 4, "int must be 4 bytes");
template<typename T>
void checkSize() {
static_assert(sizeof(T) >= 4, "Type must be at least 4 bytes");
}变参模板
// 打印任意数量的参数
template<typename... Args>
void print(Args... args) {
((std::cout << args << " "), ...); // 折叠表达式(C++17)
std::cout << "\n";
}
// 递归展开
template<typename T>
T sum(T first) {
return first;
}
template<typename T, typename... Args>
T sum(T first, Args... rest) {
return first + sum(rest...);
}
print(1, 2, 3, "hello"); // 1 2 3 hello
int total = sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 15常用特性总结
最常用的 C++11 特性:
auto类型推导- Lambda 表达式
- 智能指针(
unique_ptr,shared_ptr) - 范围 for 循环
nullptroverride关键字enum class
C++14:增量改进
C++14 是一个较小的更新,主要是对 C++11 的改进和补充。
泛型 Lambda
// C++11 只能指定具体类型
auto lambda1 = [](int x) { return x * 2; };
// C++14 支持 auto 参数
auto lambda2 = [](auto x) { return x * 2; };
lambda2(3); // int
lambda2(3.14); // doubleLambda 捕获初始化
int x = 42;
auto lambda = [y = x + 1]() { return y; };
// y 是 43,即使 x 改变也不影响
// 更复杂的捕获
auto ptr = std::make_unique<int>(100);
auto capturePtr = [p = std::move(ptr)]() { return *p; };函数返回类型推导
// C++11 必须指定返回类型
auto add1(int x, int y) -> int {
return x + y;
}
// C++14 可以推导返回类型
auto add2(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
// 递归函数需要指定返回类型
auto factorial(int n) -> int {
return n <= 1 ? 1 : n * factorial(n - 1);
}变量模板
template<typename T>
constexpr T pi = T(3.1415926535897932385);
double d = pi<double>; // 3.1415926535897932385
float f = pi<float>; // 3.1415927f
// 其他变量模板
template<typename T>
constexpr std::size_t byte_count = sizeof(T);
std::size_t size = byte_count<int>; // 4二进制字面量
int x = 0b1010; // 10
int y = 0b11111111; // 255
int z = 0b1100'0101; // 197
// 无符号
unsigned int flags = 0b0000'1111'0000'0000;数字分隔符
int million = 1'000'000;
double pi = 3.14159'26535;
int binary = 0b1010'0101;
long long credit = 1'000'000'000'000LL;
// 十六进制
uint32_t mac = 0xDE'AD'BE'EF;[[deprecated]] 属性
[[deprecated("Use newFunction instead")]]
void oldFunction() {}
// 使用
[[deprecated]] int deprecatedVar = 42;放宽 constexpr 限制
// C++14 constexpr 函数可以有局部变量和循环
constexpr int factorial(int n) {
int result = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
result *= i;
}
return result;
}
constexpr int f = factorial(5); // 120库新增特性
std::make_unique
// C++11 没有 make_unique
std::unique_ptr<int> ptr1(new int(42));
// C++14 添加了 make_unique
std::unique_ptr<int> ptr2 = std::make_unique<int>(42);
// 数组
auto arr = std::make_unique<int[]>(10);
// 更安全:异常安全
auto smartPtr = std::make_unique<MyClass>(args...);std::quoted
#include <iomanip>
#include <sstream>
std::string input = R"(Hello "World"!)";
std::stringstream ss;
ss << std::quoted(input);
std::cout << ss.str() << "\n"; // 输出: "Hello \"World\"!"
// 读取
std::string output;
ss >> std::quoted(output); // output = Hello "World"!std::exchange
// C++11 需要手动实现
template<typename T, typename U>
T exchange(T& obj, U&& newValue) {
T oldValue = std::move(obj);
obj = std::forward<U>(newValue);
return oldValue;
}
// C++14 直接使用
std::vector<int> v{1, 2, 3};
std::vector<int> old = std::exchange(v, {4, 5});
// old = {1, 2, 3}, v = {4, 5}std::integer_sequence
#include <utility>
// 编译时整数序列
template<std::size_t... Ints>
void printIndices(std::index_sequence<Ints...>) {
((std::cout << Ints << " "), ...);
}
printIndices(std::make_index_sequence<5>{}); // 0 1 2 3 4
// 应用到参数包
template<typename T, std::size_t... Is>
void printTupleElements(const T& t, std::index_sequence<Is...>) {
((std::cout << std::get<Is>(t) << " "), ...);
}chrono 和 string 字面量
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
// 时间字面量
auto duration = 100ms; // 100 毫秒
auto seconds = 2s; // 2 秒
auto minutes = 5min; // 5 分钟
auto hours = 1h; // 1 小时
// 组合使用
auto complexDuration = 1h + 30min + 45s;
// 字符串字面量(C++14)
auto str = "hello"s; // std::string
auto u8str = u8"world"s; // std::string (UTF-8)
auto wstr = L"wide"s; // std::wstringstd::shared_timed_mutex
#include <shared_mutex>
class ReaderWriter {
mutable std::shared_timed_mutex mtx_;
std::vector<int> data_;
public:
void write(int value) {
std::unique_lock<std::shared_timed_mutex> lock(mtx_);
data_.push_back(value);
}
std::vector<int> read() const {
std::shared_lock<std::shared_timed_mutex> lock(mtx_);
return data_;
}
};常用特性总结
最常用的 C++14 特性:
- 泛型 Lambda
- 函数返回类型推导
std::make_unique- 数字分隔符
- 二进制字面量
C++17:重大更新
C++17 带来了许多重要的新特性,显著提升了 C++ 的表达力和安全性。
结构化绑定
// 解构 pair
std::pair<int, std::string> p{42, "hello"};
auto [id, name] = p;
// 解构 tuple
std::tuple<int, double, std::string> t{1, 3.14, "world"};
auto [x, y, z] = t;
// 解构数组
int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3};
auto [a, b, c] = arr;
// 解构结构体
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
Point pt{10, 20};
auto [px, py] = pt;
// 在范围 for 循环中使用
std::map<std::string, int> m{{"a", 1}, {"b", 2}};
for (const auto& [key, value] : m) {
std::cout << key << ": " << value << "\n";
}if 和 switch 初始化语句
// 传统方式
std::map<int, std::string> m;
auto it = m.find(42);
if (it != m.end()) {
// 使用 it
}
// C++17 方式
if (auto it = m.find(42); it != m.end()) {
// 使用 it
}
// 配合结构化绑定
std::map<int, std::string> m{{1, "one"}, {2, "two"}};
if (auto [it, inserted] = m.emplace(3, "three"); inserted) {
std::cout << "Inserted: " << it->second << "\n";
}
// switch 初始化语句
switch (auto it = m.find(42); auto result = it->second) {
case "found":
break;
}constexpr if
template<typename T>
auto getValue(T t) {
if constexpr (std::is_pointer_v<T>) {
return *t;
} else {
return t;
}
}
int x = 42;
std::cout << getValue(x) << "\n"; // 42
std::cout << getValue(&x) << "\n"; // 42折叠表达式
// 参数包展开
template<typename... Args>
auto sum(Args... args) {
return (args + ...); // 右折叠
}
// 使用
int total = sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 15
// 左折叠
template<typename... Args>
auto printAll(Args... args) {
(std::cout << ... << args) << "\n";
}
printAll(1, " ", 2, " ", 3); // 1 2 3
// 空参数包
template<typename... Args>
void log(Args... args) {
((std::cout << args << "\n"), ...);
}内联变量
// 头文件中定义静态成员变量
struct MyClass {
static inline int value = 42; // C++17
static inline std::vector<int> data = {1, 2, 3};
};
// 全局变量
inline constexpr int MAX_SIZE = 1000;
// 不再需要在 .cpp 文件中定义类模板参数推导(CTAD)
std::pair p{42, "hello"}; // std::pair<int, const char*>
std::tuple t{1, 2.0, "three"}; // std::tuple<int, double, const char*>
// 推导指引
template<typename T>
struct MyContainer {
MyContainer(T val) : value_(val) {}
T value_;
};
MyContainer c{42}; // MyContainer<int>
// 容器推导
std::vector v{1, 2, 3}; // std::vector<int>嵌套命名空间
// C++17 之前
namespace outer::inner {
void func() {}
}
// 等同于
namespace outer {
namespace inner {
void func() {}
}
}属性改进
// [[nodiscard]]:忽略返回值会警告
[[nodiscard]] int compute() {
return 42;
}
// compute(); // 警告:返回值被忽略
// [[maybe_unused]]:抑制未使用警告
[[maybe_unused]] int x = 42;
// [[fallthrough]]:显式表示 switch 穿透
switch (value) {
case 1:
doSomething();
[[fallthrough]];
case 2:
doSomethingElse();
break;
}
// [[nodiscard("reason")]] 自定义消息
[[nodiscard("Connection must be closed")]]
Connection connect();UTF-8 字符字面量
// UTF-8 字符字面量
char8_t c1 = u8'A'; // UTF-8 编码
// UTF-8 字符串字面量
auto str = u8"Hello, 世界!"; // const char8_t*
// Unicode 编码
char16_t c2 = u'汉'; // UTF-16
char32_t c3 = U'中'; // UTF-32标准库新增特性
std::optional
#include <optional>
std::optional<int> divide(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
return std::nullopt; // 表示无值
}
return a / b;
}
auto result = divide(10, 2);
if (result) {
std::cout << *result << "\n"; // 5
}
// 使用 value_or 提供默认值
int value = divide(10, 0).value_or(-1); // -1
// 直接构造
std::optional<std::string> opt("hello");std::variant
#include <variant>
std::variant<int, double, std::string> var;
var = 42;
std::cout << std::get<int>(var) << "\n"; // 42
// 使用 std::visit
auto visitor = [](auto&& arg) {
std::cout << arg << "\n";
};
std::visit(visitor, var);
// 使用 std::holds_alternative 检查类型
if (std::holds_alternative<int>(var)) {
std::cout << "Contains int\n";
}
// 获取索引
std::cout << var.index() << "\n"; // 0std::any
#include <any>
std::any a = 42;
a = 3.14;
a = std::string("hello");
// 检查类型
if (a.type() == typeid(std::string)) {
std::cout << std::any_cast<std::string>(a) << "\n";
}
// 使用 std::any_cast
try {
int value = std::any_cast<int>(a); // 抛出异常
} catch (const std::bad_any_cast& e) {
std::cout << "Bad cast: " << e.what() << "\n";
}std::string_view
#include <string_view>
// 避免字符串拷贝
void printString(std::string_view sv) {
std::cout << sv << "\n";
}
std::string str = "hello";
const char* cstr = "world";
printString(str); // OK
printString(cstr); // OK
printString("test"); // OK
// 子串操作
std::string_view sv = "Hello, World!";
std::cout << sv.substr(0, 5) << "\n"; // Hello
std::cout << sv.starts_with("Hello") << "\n"; // truestd::byte
#include <cstddef>
// 字节类型,用于访问原始内存
std::byte b{42};
std::byte data[4];
data[0] = std::byte{0x12};
data[1] = std::byte{0x34};
// 转换为整数
int value = std::to_integer<int>(data[0]); // 18
// 内存操作
std::memset(data, std::byte{0}, sizeof(data));std::invoke
#include <functional>
// 调用函数指针
int add(int a, int b) { return a + b; }
int result = std::invoke(add, 3, 4); // 7
// 调用成员函数
struct Calculator {
int multiply(int a, int b) { return a * b; }
};
Calculator calc;
int product = std::invoke(&Calculator::multiply, calc, 3, 4); // 12
// 调用 lambda
auto lambda = [](int a, int b) { return a * b; };
int lambdaResult = std::invoke(lambda, 5, 6); // 30std::apply
#include <tuple>
int add(int a, int b, int c) { return a + b + c; }
auto t = std::make_tuple(1, 2, 3);
int result = std::apply(add, t); // 6
// 访问 tuple 元素
std::apply([](auto&... args) {
((std::cout << args << "\n"), ...);
}, t);std::make_from_tuple
#include <tuple>
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
int z;
};
auto t = std::make_tuple(1, 2, 3);
Point p = std::make_from_tuple<Point>(t); // Point{1, 2, 3}std::clamp
#include <algorithm>
int value = 75;
int minVal = 0;
int maxVal = 100;
int clamped = std::clamp(value, minVal, maxVal); // 75
int clamped2 = std::clamp(-10, minVal, maxVal); // 0
int clamped3 = std::clamp(150, minVal, maxVal); // 100
// 带比较函数
auto clamped4 = std::clamp(value, minVal, maxVal, std::greater<int>());std::reduce/std::transform_reduce
#include <numeric>
#include <execution>
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// 并行归约
int sum = std::reduce(std::execution::par, vec.begin(), vec.end());
// 先转换后归约
auto squaredSum = std::transform_reduce(
std::execution::par,
vec.begin(), vec.end(),
0LL,
std::plus<>{},
[](int x) { return x * x; }
); // 55 (1+4+9+16+25)std::filesystem
#include <filesystem>
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
// 创建目录
fs::create_directory("test");
fs::create_directories("a/b/c"); // 递归创建
// 遍历目录
for (const auto& entry : fs::directory_iterator(".")) {
std::cout << entry.path() << "\n";
std::cout << "Is file: " << entry.is_regular_file() << "\n";
}
// 检查文件
if (fs::exists("file.txt")) {
std::cout << "File size: " << fs::file_size("file.txt") << "\n";
}
// 路径操作
fs::path p = "/home/user/documents/file.txt";
std::cout << "Filename: " << p.filename() << "\n";
std::cout << "Extension: " << p.extension() << "\n";
std::cout << "Parent: " << p.parent_path() << "\n";
// 相对路径
std::cout << "Relative: " << fs::relative(p) << "\n";std::scoped_lock
#include <mutex>
std::mutex mtx1, mtx2;
// C++17 之前:手动 lock
std::lock(mtx1, mtx2);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock1(mtx1, std::adopt_lock);
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock2(mtx2, std::adopt_lock);
// C++17:scoped_lock 自动管理多个锁
std::scoped_lock lock(mtx1, mtx2);
// 自动以避免死锁的方式获取所有锁
// 析构时自动释放__has_include
#if __has_include(<optional>)
#include <optional>
#endif
#if __has_include(<filesystem>) && __has_include(<version>)
#include <filesystem>
#define HAS_FILESYSTEM 1
#else
#define HAS_FILESYSTEM 0
#endif并行算法
#include <algorithm>
#include <execution>
std::vector<int> vec(1000000);
std::iota(vec.begin(), vec.end(), 0);
// 执行策略
std::sort(std::execution::par, vec.begin(), vec.end()); // 并行
std::sort(std::execution::seq, vec.begin(), vec.end()); // 顺序
std::sort(std::execution::par_unseq, vec.begin(), vec.end()); // 并行+向量化
// 并行查找
auto it = std::find(std::execution::par, vec.begin(), vec.end(), 42);
// 并行变换
std::transform(std::execution::par, vec.begin(), vec.end(), vec.begin(),
[](int x) { return x * 2; });std::shared_mutex
#include <shared_mutex>
class ThreadSafeCache {
mutable std::shared_mutex mtx_;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> cache_;
public:
// 读操作:使用共享锁
std::string read(const std::string& key) const {
std::shared_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mtx_);
auto it = cache_.find(key);
return it != cache_.end() ? it->second : "";
}
// 写操作:使用独占锁
void write(const std::string& key, const std::string& value) {
std::unique_lock<std::shared_mutex> lock(mtx_);
cache_[key] = value;
}
};常用特性总结
最常用的 C++17 特性:
- 结构化绑定
std::optionalstd::variantstd::string_viewstd::invoke- if 初始化语句
std::filesystem[[nodiscard]]属性
C++20:革命性更新
C++20 是继 C++11 之后最大的更新,引入了模块、协程、概念和 ranges 等重大特性。
Concepts(概念)
#include <concepts>
// 定义概念
template<typename T>
concept Integral = std::is_integral_v<T>;
template<typename T>
concept Addable = requires(T a, T b) {
a + b; // 必须支持 + 运算
};
// 使用概念约束模板
template<Integral T>
T add(T a, T b) {
return a + b;
}
// requires 子句
template<typename T>
requires Addable<T>
T multiply(T a, T b) {
return a * b;
}
// 简写语法
auto subtract = [](std::integral auto a, std::integral auto b) {
return a - b;
};
// 标准概念
template<std::sortable T>
void sortContainer(std::vector<T>& vec) {
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
}Ranges(范围库)
#include <ranges>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
// 过滤偶数
auto evens = vec | std::views::filter([](int x) { return x % 2 == 0; });
// 转换
auto squared = evens | std::views::transform([](int x) { return x * x; });
// 取前 3 个
auto result = squared | std::views::take(3);
// 链式调用
auto final = vec
| std::views::filter([](int x) { return x % 2 == 0; })
| std::views::transform([](int x) { return x * x; })
| std::views::take(3);
// 使用
for (auto x : final) {
std::cout << x << " "; // 4 16 36
}
// 直接创建视图
auto view = std::views::iota(1, 10) | std::views::filter([](int x) { return x % 2; });协程(Coroutines)
#include <coroutine>
#include <iostream>
// 简单的生成器
template<typename T>
struct Generator {
struct promise_type {
T value;
Generator get_return_object() {
return Generator{std::coroutine_handle<promise_type>::from_promise(*this)};
}
std::suspend_always initial_suspend() { return {}; }
std::suspend_always final_suspend() noexcept { return {}; }
std::suspend_always yield_value(T val) {
value = val;
return {};
}
void return_void() {}
void unhandled_exception() { std::terminate(); }
};
std::coroutine_handle<promise_type> h;
Generator(std::coroutine_handle<promise_type> handle) : h(handle) {}
~Generator() { if (h) h.destroy(); }
bool next() {
h.resume();
return !h.done();
}
T value() { return h.promise().value; }
};
Generator<int> range(int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
co_yield i;
}
}
// 使用
auto gen = range(1, 5);
while (gen.next()) {
std::cout << gen.value() << " "; // 1 2 3 4
}模块(Modules)
// math.ixx (模块接口)
export module math;
export int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
export int multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
// main.cpp
import math;
import <iostream>;
int main() {
std::cout << add(2, 3) << "\n"; // 5
return 0;
}三路比较运算符(<=>)
#include <compare>
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
// 自动生成所有比较运算符
auto operator<=>(const Point&) const = default;
};
Point p1{1, 2};
Point p2{1, 3};
if (p1 < p2) { /* ... */ }
if (p1 == p2) { /* ... */ }
if (p1 != p2) { /* ... */ }
// 自定义比较
struct Version {
int major;
int minor;
int patch;
std::strong_ordering operator<=>(const Version& other) const {
if (auto cmp = major <=> other.major; cmp != 0) return cmp;
if (auto cmp = minor <=> other.minor; cmp != 0) return cmp;
return patch <=> other.patch;
}
};Designated Initializers(指定初始化器)
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
int z;
};
Point p{.x = 1, .z = 3}; // y 初始化为 0
// 数组
int arr[5] = {[1] = 10, [3] = 30}; // {0, 10, 0, 30, 0}
// 结构体数组
Point points[] = {{.x = 1}, {.y = 2}, {.z = 3}};consteval 和 constinit
// consteval:必须在编译期求值
consteval int square(int x) {
return x * x;
}
constexpr int result = square(5); // OK
// int x = 5;
// int y = square(x); // 编译错误,x 不是常量
// constinit:必须在编译期初始化
constinit int global = 42;
// 结合使用
consteval int compute(int x) { return x * 2; }
constinit int computed = compute(42);范围 for 循环支持初始化器
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// C++20 之前
for (auto& elem : vec) {
elem *= 2;
}
// C++20:在循环中声明变量
for (auto vecCopy = vec; auto& elem : vecCopy) {
// 使用 vecCopy
elem *= 2;
}
// 更复杂的用法
for (auto it = vec.begin(), end = vec.end(); auto& elem : vec) {
// 使用 it 和 end
}Lambda 模板参数列表
// C++20 之前
auto lambda1 = [](auto x) { return x * 2; };
// C++20:显式模板参数
auto lambda2 = []<typename T>(T x) { return x * 2; };
// 多个模板参数
auto lambda3 = []<typename T, typename U>(T a, U b) {
return a + b;
};
// 模板参数默认值
auto lambda4 = []<typename T = int>(T x) { return x; };
// 在 requires 子句中使用
auto lambda5 = []<typename T>(T x) requires std::integral<T> {
return x * 2;
};[[no_unique_address]] 属性
struct Empty {};
struct A {
int x;
Empty e; // 不占用空间
};
struct B {
int x;
[[no_unique_address]] Empty e; // 编译器可以优化,不占用额外空间
};
// 编译器可能将 B 的大小优化为与 int 相同
static_assert(sizeof(B) == sizeof(int));[[likely]] 和 [[unlikely]] 属性
int process(int value) {
switch (value) {
[[likely]] case 1:
return 10;
[[unlikely]] case 2:
return 20;
default:
return 0;
}
}
bool check(int x) {
if (x > 0) [[likely]] {
return true;
}
return false;
}
void logMessage(int level) {
if (level > 100) [[unlikely]] {
// 警告:这很少见
}
}标准库新增特性
std::format
#include <format>
std::string name = "Alice";
int age = 30;
// 类似 Python 的格式化
std::string s1 = std::format("Name: {}, Age: {}", name, age);
// 带索引
std::string s2 = std::format("{1} is {0} years old", age, name);
// 格式化选项
std::string s3 = std::format("Pi: {:.2f}", 3.14159); // Pi: 3.14
std::string s4 = std::format("Hex: {:#x}", 255); // Hex: 0xff
std::string s5 = std::format("Padding: {:>10}", "test"); // Padding: test
std::string s6 = std::format("Zeros: {:0>5}", 42); // Zeros: 00042std::span
#include <span>
void processArray(std::span<int> arr) {
for (auto x : arr) {
std::cout << x << " ";
}
}
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
processArray(arr); // OK
processArray(vec); // OK
// 子视图
std::span<int> sub(arr, 3); // 前 3 个元素
// 动态大小
std::span<int> dynamic(vec.data(), vec.size());std::source_location
#include <source_location>
void log(const std::string& msg,
std::source_location loc = std::source_location::current()) {
std::cout << loc.file_name() << ":" << loc.line() << " "
<< loc.function_name() << ": " << msg << "\n";
}
void foo() {
log("Hello"); // 自动记录调用位置
}std::bit_cast
#include <bit>
// 类型重新解释
float f = 3.14f;
uint32_t bits = std::bit_cast<uint32_t>(f);
// 位反转
struct Packed {
uint32_t x : 10;
uint32_t y : 10;
uint32_t z : 10;
};
uint32_t raw = 0xABCDEF;
Packed p = std::bit_cast<Packed>(raw);std::endian
#include <bit>
// 检查字节序
if (std::endian::native == std::endian::little) {
// 小端字节序
}
// 字节序转换
uint32_t x = 0x12345678;
uint32_t swapped = std::byteswap(x);std::make_shared 支持数组
// C++20 之前
auto arr = std::make_shared<std::vector<int>>(10, 0);
// C++20 支持数组
auto arr2 = std::make_shared<int[]>(10);
arr2[0] = 1;
arr2[1] = 2;
// 多维数组
auto matrix = std::make_shared<int[][3]>(5);contains 成员函数
std::set<int> s = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
// C++20 之前
if (s.find(3) != s.end()) { /* ... */ }
// C++20
if (s.contains(3)) { /* ... */ }
// 同样适用于 map, unordered_map, unordered_set
std::map<std::string, int> m{{"a", 1}, {"b", 2}};
if (m.contains("a")) { /* ... */ }starts_with 和 ends_with
std::string str = "Hello, World!";
if (str.starts_with("Hello")) { /* ... */ }
if (str.ends_with("!")) { /* ... */ }
// 同样适用于 string_view
std::string_view sv = "test.txt";
if (sv.ends_with(".txt")) { /* ... */ }
// C++23 也添加到了 std::string::contains并发特性
std::jthread
#include <thread>
std::jthread jt([](std::stop_token st) {
while (!st.stop_requested()) {
// 执行任务
}
});
// 析构时自动 join
// 或者显式请求停止
jt.request_stop();std::stop_token
#include <thread>
void worker(std::stop_token st, int id) {
while (!st.stop_requested()) {
// 工作
std::this_thread::sleep_for(100ms);
}
}
std::jthread t1(worker, 1);
std::jthread t2(worker, 2);
// 请求停止
t1.request_stop();
t2.request_stop();
// 所有 jthread 析构时自动 join信号量(Semaphores)
#include <semaphore>
std::counting_semaphore<5> sem(5); // 最多 5 个许可
void worker() {
sem.acquire(); // 获取许可
// 临界区
sem.release(); // 释放许可
}
// 二进制信号量
std::binary_semaphore bs(1);
std::binary_semaphore bs2(0); // 初始为 0Barriers
#include <barrier>
auto phase1 = [] { /* 第一阶段工作 */ };
auto phase2 = [] { /* 第二阶段工作 */ };
std::barrier barrier(2, [] { /* 阶段完成回调 */ });
std::thread t1([&] {
phase1();
barrier.arrive_and_wait(); // 等待 t2
phase2();
});
std::thread t2([&] {
phase1();
barrier.arrive_and_wait(); // 等待 t1
phase2();
});Latches
#include <latch>
std::latch workDone(3); // 3 个工作线程
void worker(int id) {
// 做工作
workDone.count_down(); // 标记完成
}
void master() {
// 等待所有工作完成
workDone.wait();
// 继续
}Atomic wait/notify
#include <atomic>
std::atomic<int> counter{0};
// 等待直到值改变
int oldValue = counter.load();
while (counter.wait(oldValue) == oldValue) {
// 值未改变,继续等待
}
// 通知所有等待的线程
counter.store(1);
counter.notify_all();std::atomic<std::shared_ptr>
#include <atomic>
#include <memory>
struct Node {
int value;
std::atomic<std::shared_ptr<Node>> next;
};
std::atomic<std::shared_ptr<Node>> head;
// 原子地读取
std::shared_ptr<Node> current = head.load();
// 原子地 CAS
std::shared_ptr<Node> newNode = std::make_shared<Node>();
std::shared_ptr<Node> expected = head.load();
do {
newNode->next = expected;
} while (!head.compare_exchange_weak(expected, newNode));常用特性总结
最常用的 C++20 特性:
- Concepts(概念)
- Ranges(范围库)
- 三路比较运算符(
<=>) std::formatstd::spancontains成员函数starts_with/ends_withstd::jthread
C++23:最新特性
C++23 是最新的标准,继续完善和扩展 C++ 的功能。
Deducing this(推导 this)
struct Widget {
void process(this auto&& self) {
// self 可以是左值引用、右值引用或 const 引用
self.doSomething();
}
void doSomething() & {
std::cout << "Lvalue\n";
}
void doSomething() && {
std::cout << "Rvalue\n";
}
};
Widget w;
w.process(); // Lvalue
Widget{}.process(); // Rvalueif consteval
constexpr int compute(int x) {
if consteval {
// 编译期执行的代码
return x * 2;
} else {
// 运行期执行的代码
return x * 3;
}
}
constexpr int result = compute(5); // 10 (编译期)
int runtime = compute(5); // 15 (运行期)auto(x) 和 auto{x}
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3};
// 强制拷贝
auto copy = auto(vec); // vec 的副本
// 强制移动
auto moved = auto(std::move(vec)); // 移动构造
// 括号形式
auto copy2 = auto{vec};静态运算符(Static Operators)
struct Number {
int value;
static Number operator+(Number a, Number b) {
return Number{a.value + b.value};
}
static Number operator-(Number a, Number b) {
return Number{a.value - b.value};
}
};
Number n1{1};
Number n2{2};
Number n3 = n1 + n2; // Number{3}
Number n4 = n1 - n2; // Number{-1}多维 operator[]
// C++23 之前
data[0][1][2];
// C++23:支持多维 operator[]
template<typename T>
class Tensor3D {
T* data_;
std::size_t dim1_, dim2_, dim3_;
public:
Tensor3D(T* data, std::size_t d1, std::size_t d2, std::size_t d3)
: data_(data), dim1_(d1), dim2_(d2), dim3_(d3) {}
// C++23 多维 operator[]
auto operator[](std::size_t i) requires std::is_array_v<T> {
return std::mdspan(data_ + i * dim2_ * dim3_, dim2_, dim3_);
}
};[[assume]] 属性
int divide(int a, int b) {
[[assume(b != 0)]]; // 告诉编译器 b 不为 0
return a / b;
}
int process(int value) {
if (value < 0 || value > 100) [[assume(false)]];
// 编译器知道 value 在 [0, 100] 范围内
return value * 2;
}size_t 字面量后缀
// C++23 字面量后缀
using namespace std::literals;
std::size_t a = 123uz; // size_t
std::size_t b = 0uz; // 空指针安全的 size_t
// 与 sizeof 配合
auto size = sizeof(int)uz;std::print 和 std::println
#include <print>
std::print("Hello, World!\n");
std::println("Hello, World!"); // 自动换行
// 格式化
std::println("Name: {}, Age: {}", "Alice", 30);
// 支持容器
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3};
std::println("Vector: {}", vec); // Vector: [1, 2, 3]
// 支持格式化选项
std::println("Pi: {:.2f}", 3.14159); // Pi: 3.14
std::println("Binary: {:b}", 42); // Binary: 101010
// 输出到文件
std::println(stdout, "To stdout");标准库模块
// 导入标准库模块而不是头文件
import std;
// 不再需要 #include <iostream>, <vector>, 等
int main() {
std::println("Hello, World!");
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 2, 3};
return 0;
}std::expected
#include <expected>
std::expected<int, std::string> divide(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
return std::unexpected("Division by zero");
}
return a / b;
}
auto result = divide(10, 2);
if (result) {
std::println("Result: {}", *result);
} else {
std::println("Error: {}", result.error());
}
// 使用 value_or
int value = divide(10, 0).value_or(-1);
// 链式操作
auto final = divide(10, 2).transform([](int x) { return x * 2; });std::generator
#include <generator>
std::generator<int> range(int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i < end; ++i) {
co_yield i;
}
}
for (auto x : range(1, 5)) {
std::println("{}", x); // 1 2 3 4
}
// 生成器组合
std::generator<int> fibonacci() {
int a = 0, b = 1;
while (true) {
co_yield a;
auto next = a + b;
a = b;
b = next;
}
}std::mdspan
#include <mdspan>
int data[12] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12};
// 3x4 矩阵视图
std::mdspan<int, std::extents<std::size_t, 3, 4>> mat(data);
std::println("mat[1][2] = {}", mat[1][2]); // 7
// 动态维度
std::mdspan<int, std::dextents<std::size_t, 2>> dyn(data, 3, 4);
// 切片视图
std::mdspan row = std::submdspan(mat, std::slice{1, 1, 2}); // 第一行的一部分std::flat_map 和 std::flat_set
#include <flat_map>
#include <flat_set>
// 扁平化容器,使用排序的 vector 存储
std::flat_map<std::string, int> map;
map["a"] = 1;
map["b"] = 2;
// 保持排序
map.sort(); // 按键排序
// 快速查找
if (map.contains("a")) {
auto it = map.find("a");
}
std::flat_set<int> set = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5}; // 自动去重和排序
// 范围操作
auto range = map.equal_range("b");std::byteswap
#include <bit>
uint32_t x = 0x12345678;
uint32_t y = std::byteswap(x); // 0x78563412
// 大小端转换
uint16_t a = 0xABCD;
uint16_t swapped = std::byteswap(a); // 0xCDABstd::to_underlying
#include <type_traits>
enum class Color : int { Red = 1, Green = 2, Blue = 3 };
Color c = Color::Red;
int value = std::to_underlying(c); // 1
// 强转等价但更清晰
auto val = std::to_underlying(Color::Green); // 2std::string::contains
std::string str = "Hello, World!";
// C++23 之前
if (str.find("World") != std::string::npos) { /* ... */ }
// C++23
if (str.contains("World")) { /* ... */ }
if (str.contains('o')) { /* ... */ }
// string_view 也有 contains
std::string_view sv = "test.txt";
if (sv.contains("test")) { /* ... */ }std::unreachable
#include <utility>
int process(int value) {
switch (value) {
case 1:
return 10;
case 2:
return 20;
default:
std::unreachable(); // 告诉编译器这里不可达
}
}
void* allocate(std::size_t size) {
if (size == 0) {
return nullptr;
}
// 编译器知道 size > 0
std::unreachable();
}常用特性总结
最常用的 C++23 特性:
std::print和std::printlnstd::expectedstd::generatorstd::flat_map和std::flat_set- 标准库模块(
import std) std::byteswapstd::string::contains
日常开发必备
C++11:
auto- 几乎无处不在- Lambda 表达式 - 回调和算法
- 智能指针 - 资源管理
- 范围 for 循环 - 遍历容器
nullptr- 空指针override- 虚函数重写
C++14:
- 泛型 Lambda - 更灵活的 lambda
std::make_unique- 创建 unique_ptr- 数字分隔符 - 提高可读性
C++17:
- 结构化绑定 - 解构返回值
std::optional- 可选值std::string_view- 避免字符串拷贝std::invoke- 统一调用接口std::filesystem- 文件系统操作[[nodiscard]]- 防止忽略返回值
C++20:
- Concepts - 模板约束
- Ranges - 函数式风格处理序列
std::format- 格式化输出std::span- 数组视图contains- 容器查找
C++23:
std::print/std::println- 简化输出std::expected- 错误处理std::generator- 生成器
兼容性考虑
- C++11 - 所有现代编译器完全支持
- C++14 - GCC 5+, Clang 3.4+, MSVC 2015+
- C++17 - GCC 7+, Clang 5+, MSVC 2017 15.8+
- C++20 - GCC 10+, Clang 12+, MSVC 2022 16.10+
- C++23 - GCC 13+, Clang 16+, MSVC 2022 17.5+